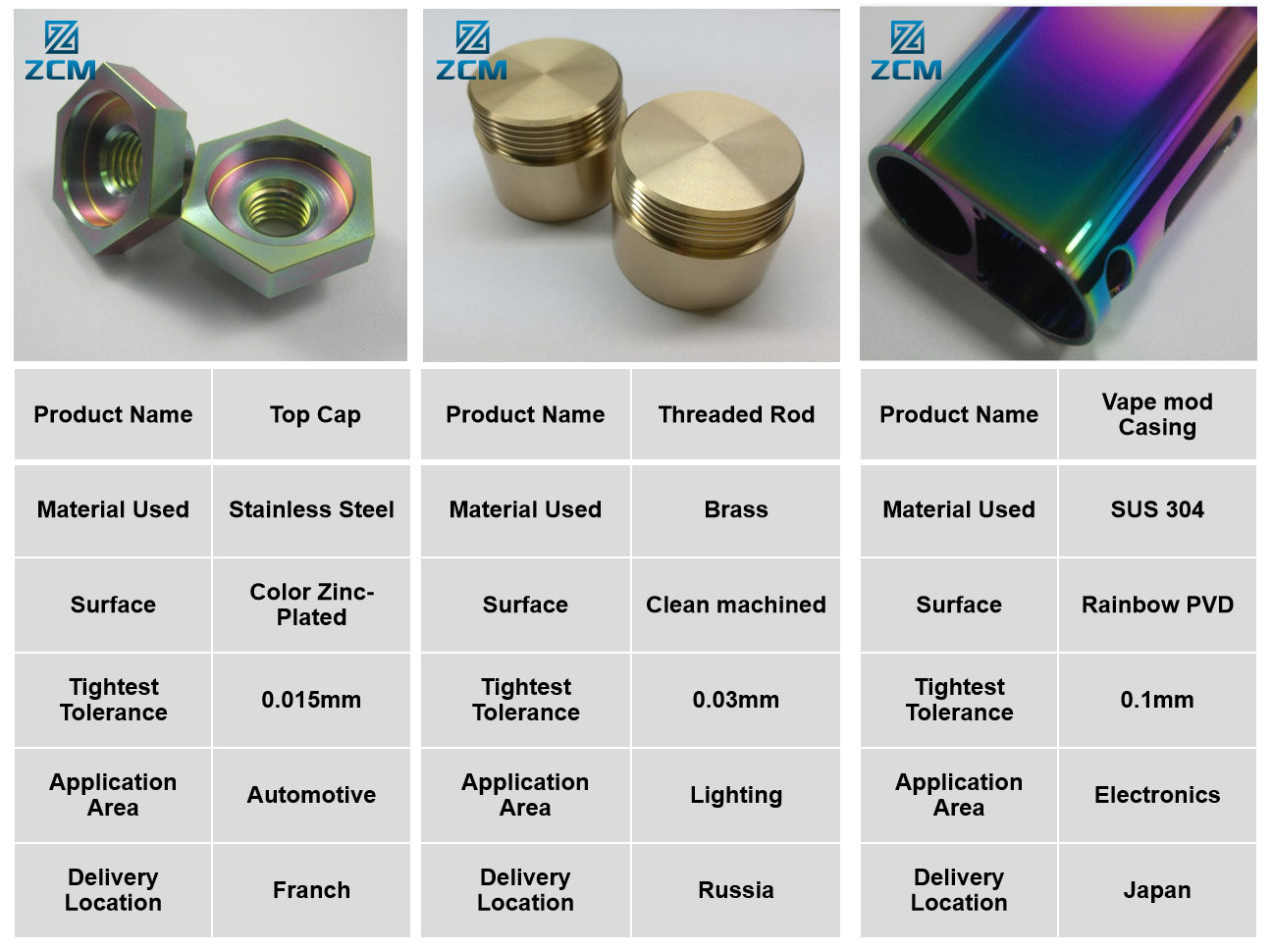
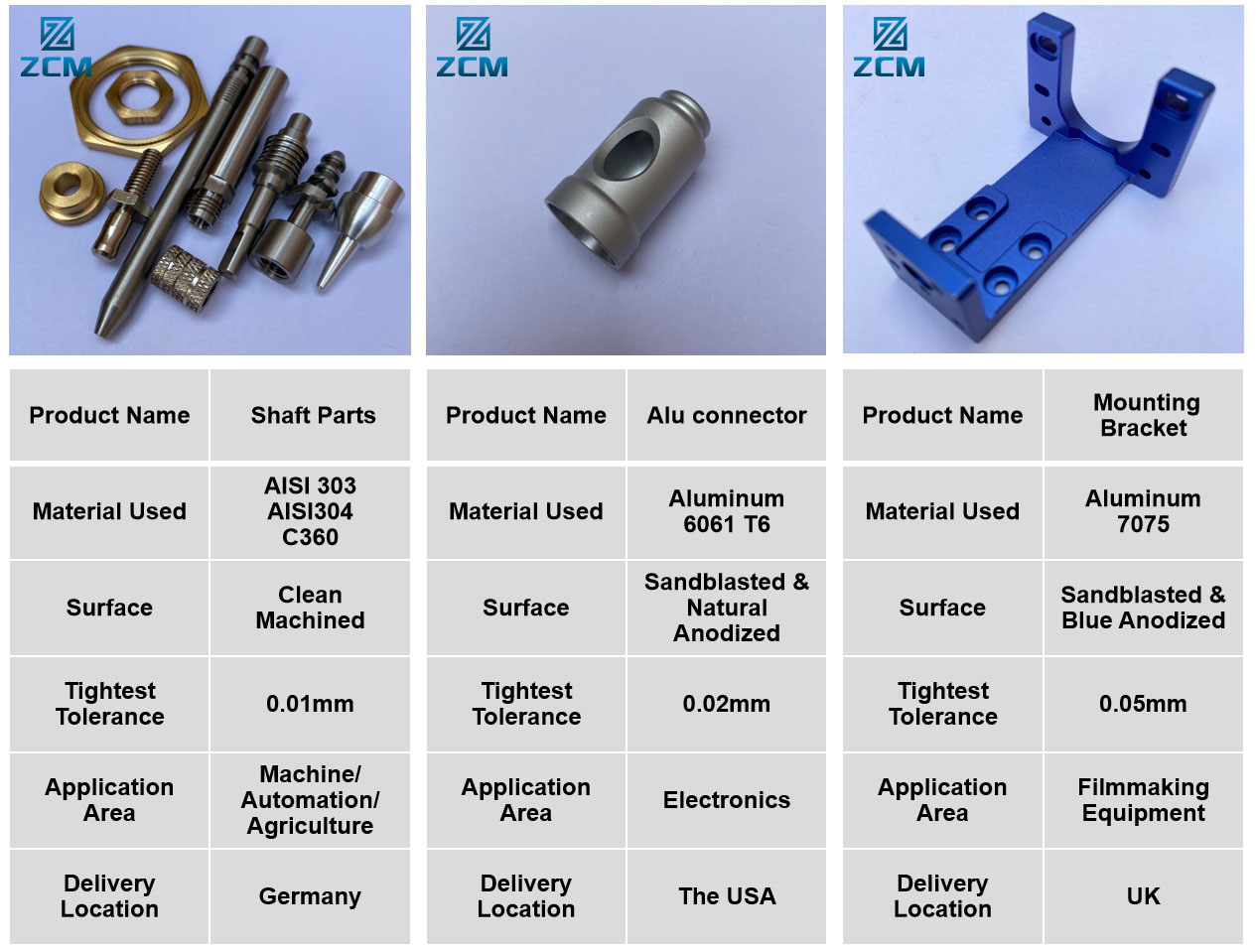
Surface Finishes
Surface Finishes
As-Machined: The most popular and cost efficient way for inner functional components. Fine and even tool path is also good for aspect parts.
Bead Blasted: the process or operation of propelling a stream of abrasive material composed of high-velocity sand-sizes particles against the metal surface under high pressure with blast equipment like air pressure system, to remove surface contaminants, clean metals or increase a texture, then change the smoothness or roughness of surface. The part is left with a matt appearance. Range of 120 to 320 beads allows us to create different roughness to the surface.
Anodizing/Anodized: an electrolytic passivation process of forming a thin layer of aluminum oxide on the exterior of aluminum CNC machined parts to increase the thickness of the natural oxide layer and protect the metal, as the layer has higher corrosion and abrasion resistance than aluminum.
Powder Coat: This is a process where powdered paint is sprayed onto a part which is then baked in an oven. This creates a strong, wear- and corrosion-resistant layer that is more durable than standard painting methods. A wide variety of colors are available to create the desired aesthetic.
Painting: refers to an altering surface finishing process, spraying paint, pigment, or color to a solid surface as a colored protective layer, and can be done on metal or non-metal CNC machined components of any shapes, usually applied on aluminum, stainless steel and steel alloy parts. The purpose is to improve aesthetic appearance and prevent corrosion or oxidation.
Passivation: a common chemical surface treatment method for steel and stainless steel, to remove ferrous contaminants or use a light coat of protective material to create a shell for enhancing the corrosion resistance or reducing the chemical reactivity.
Electroplating/Plating: a process of using an electric current to reduce dissolved metal cations so that they form a thin coherent metal coating on an electrode, to change the properties of the machining metal surface or build up thickness for undersized parts.
Powder coating/Powder coat: a functional and decorative finish, which is applied as a free-flowing, dry powder, employs electrostatically and then cured under heat, to create a hard finish that is tougher than conventional paint. The main applications including household appliances, aluminum extrusions, drum hardware, automobile, motorcycle, and bicycle parts.
Polishing: also known as buffing, a process of rubbing the surface of parts or utilizing a chemical action to produce a smooth and shiny surface, make the surface get significant specular reflection or reduce diffuse reflection in some materials.
Black oxide/Blackening : gun bluing or hot blackening, a chemical process of forming a black conversion coating on stainless steel, copper and copper based alloys, zinc, powdered metals, silver solder, and ferrous materials, to improve corrosion resistance and minimize light reflection.
Conversion coating/Chromate conversion : the coating are used for metals converted to a protective layer through the chemical or electrochemical processes, primarily used as a corrosion inhibitor, decorative finish, or to retain electrical conductivity.